EMERGENCy & NEW PATIENTS Welcome! - Lititz
Gum Disease – Lititz, PA
Gum Disease
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is an infection that affects the gums around your teeth. It is a leading cause of tooth loss in adults and can be difficult to identify since it typically does not cause pain. Your dentist will examine for signs of gum disease during routine checkups by measuring the space between your teeth and gums.
What causes gum disease?
Plaque buildup on the teeth is the main cause of gum disease. If not properly removed through flossing, brushing, and regular dental checkups, plaque can release toxins that harm the gums. Periodontal disease develops below the gum line, forming pockets that detach the gums from the teeth. The disease advances through two stages: gingivitis and periodontitis.
- Gingivitis is the initial phase of gum disease, characterized by red, swollen gums that bleed easily. With regular daily brushing and flossing, gingivitis can be effectively treated and typically eliminated altogether.
- Failure to treat gingivitis can lead to periodontitis, which can result in permanent damage to the gums and bone that support the teeth. This condition may ultimately cause teeth to become loose, fall out, or require extraction by a dentist.

Certain factors can increase a patient's risk of developing periodontal disease, including:
Avoid smoking or using chewing tobacco.
Diabetes
Certain medications, such as steroids, anti-epilepsy drugs, cancer therapy drugs, calcium channel blockers, and oral contraceptives, can produce distinct effects on the body.
Bridges that are no longer the right size
Crooked teeth
Old fillings
Pregnancy
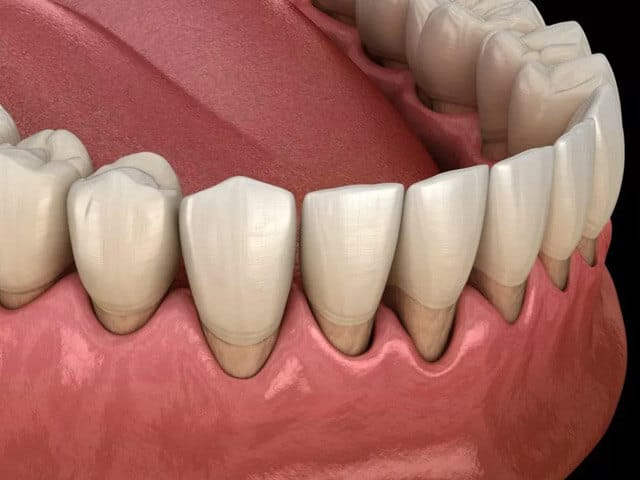
While it is possible to have periodontal disease and not know it, some symptoms can include:
- Easy bleeding gums
- Gums that are red, swollen, and tender
- Teeth with receding gums
- Persistent halitosis or unpleasant taste in the mouth
- There is pus trapped between your teeth and gums.
- Your permanent teeth are loose or separating.
- If there is any alteration in the way your teeth align when you bite
- If there are any changes in the fit of your partial dentures
Treating Gum Disease
Various treatment options are available for gum disease, and the specific method chosen depends on the severity of the case. Some common treatments include:
- Non-surgical treatments such as scaling and root planing (deep cleaning)
- Services offered include periodontal surgery and laser gum surgery
- Dental implants
Preventing Gum Disease
It is important to have regular dental checkups and periodontal examinations to maintain your overall health and the health of your smile. By practicing good oral hygiene at home, such as regular brushing, flossing, and eating a balanced diet, you can reduce your risk of gum disease. Remember to schedule regular dental visits to keep your smile healthy and bright.
