EMERGENCy & NEW PATIENTS Welcome! - Wyomissing
Gum Disease – Wyomissing, PA
Gum Disease
Gum disease, or periodontal disease, is a prevalent infection that impacts the gums surrounding your teeth. It can result in tooth loss in adults and is frequently symptomless. Your dentist will check for signs of gum disease during routine checkups by measuring the space between your teeth and gums.
What causes gum disease?
Gum disease develops due to the buildup of plaque, a sticky bacteria that sticks to the teeth. If not consistently removed through flossing, brushing, and dental check-ups, plaque can accumulate and release harmful toxins that harm the gums. Periodontal disease forms below the gum line, causing pockets to form between the gums and teeth. This disease has two stages.
- The early stage of gum disease, known as gingivitis, is identified by red, swollen gums that bleed easily. Consistent brushing and flossing can effectively treat and often eliminate this condition.
- Failure to treat gingivitis can lead to periodontitis, a condition that causes significant damage to the gums and supporting bone of the teeth. If left untreated, periodontitis can result in loose teeth, tooth loss, or the requirement for extraction by a dentist. Seeking professional treatment is essential to avoid additional harm to oral health.

Certain factors can increase a patient's risk of developing periodontal disease, including:
Smoking or using chewing tobacco
Diabetes
Certain medications such as steroids, anti-epileptic drugs, cancer therapy drugs, calcium channel blockers, and oral contraceptives.
Bridges that no longer fit properly
Crooked teeth
Old fillings
Pregnancy
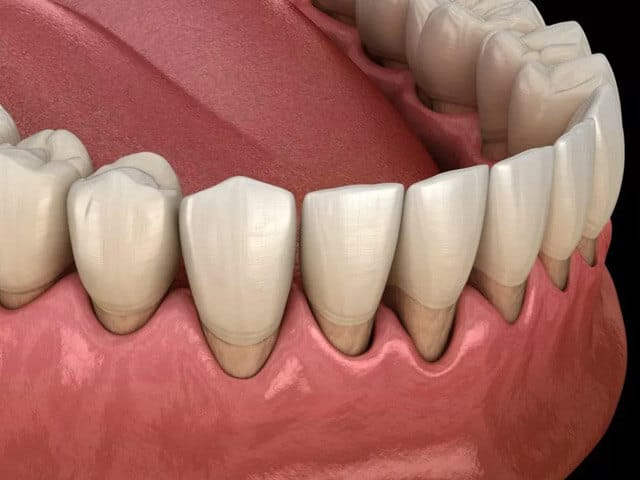
While it is possible to have periodontal disease and not know it, some symptoms can include:
- Gums that bleed easily
- Red, swollen, and sensitive gums.
- Receding gums can cause teeth to appear longer.
- Persistent bad breath or unpleasant taste
- You have pus trapped between your teeth and gums.
- Your adult teeth are loose or separating.
- If you observe any changes in the alignment of your teeth when you bite.
- Please let us know if there are any changes in the fit of your partial dentures.
Treating Gum Disease
Gum disease can be treated in a variety of ways, with the specific treatment depending on the severity of the case. Some common treatments include:
- Non-surgical treatments such as scaling and root planing (deep cleaning)
- Periodontal surgery and laser gum surgery are both options for treatment.
- Dental implants
Preventing Gum Disease
Regular dental checkups and periodontal examinations are essential for maintaining both your overall health and the health of your smile. Practicing good oral hygiene at home can help prevent tooth loss from periodontal disease. Remember to brush your teeth regularly, clean between your teeth, eat a balanced diet, and schedule regular dental visits to keep your smile healthy.
